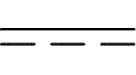
This is an image of the DC symbol.
Things to bear in mind:
1) You will never plug a DC power pack to a AC device! Never MIX! In other words, AC goes with AC, DC power pack goes with DC device.
2) Voltages on the device and the power pack have to match. (eg: 12V on the device and 12 V on the power pack)
3) A stands for amperage, the amperage on the power pack must be greater than the amerage on th device otherwise you don't get enough power!
4) You look the output on the adaptor and the input on the device
5) Sometimes you need to look at the symbols to find out whether it's a DC or AC adaptor.
Examples:
Find a power pack for this Thin Client: input DC 12V 3.33A
Power adaptor 1: 4.5V 600mA -> won't match because 4.5V < 12V
Power adaptor 2: 12V 2.0 A -> 12V is ok but it won't match because 2.0A < 3.33A, the amperage has to be greater than the thin client's input amerage.
Answer: the power pack must have an output of 12V and amerage > 3.33A
Other things useful to know:
Most Adaptors (not all) are DC.
Car Batteries are DC.
1000mA = 1A
660mA = 0.66A
3.33A = 3330mA
AC stands for Alternating Current
DC stands for Direct Current
All the batteries in the wolrd are DC.
V= Voltage = pressure of the wire