AD Domains and Trusts
domain.msc
Active Directory Management
admgmt.msc
AD Sites and Serrvices
dssite.msc
AD Users and COmputers
dsa.msc
ADSI Edit
adsiedit.msc
Authorization manager
azman.msc
Certification Authority Management
certsrv.msc
Certificate Templates
certtmpl.msc
Cluster Administrator
cluadmin.exe
Computer Management
compmgmt.msc
Component Services
comexp.msc
Configure Your Server
cys.exe
Device Manager
devmgmt.msc
DHCP Managment
dhcpmgmt.msc
Disk Defragmenter
dfrg.msc
Disk Manager
diskmgmt.msc
Distributed File System
dfsgui.msc
DNS Managment
dnsmgmt.msc
Event Viewer
eventvwr.msc
Indexing Service Management
ciadv.msc
IP Address Manage
ipaddrmgmt.msc
Licensing Manager
llsmgr.exe
Local Certificates Management
certmgr.msc
Local Group Policy Editor
gpedit.msc
Local Security Settings Manager
secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups Manager
lusrmgr.msc
Network Load balancing
nlbmgr.exe
Performance Montior
perfmon.msc
PKI Viewer
pkiview.msc
Public Key Managment
pkmgmt.msc
QoS Control Management
acssnap.msc
Remote Desktops
tsmmc.msc
Remote Storage Administration
rsadmin.msc
Removable Storage
ntmsmgr.msc
Removalbe Storage Operator Requests
ntmsoprq.msc
Routing and Remote Access Manager
rrasmgmt.msc
Resultant Set of Policy
rsop.msc
Schema management
schmmgmt.msc
Services Management
services.msc
Shared Folders
fsmgmt.msc
SID Security Migration
sidwalk.msc
Telephony Management
tapimgmt.msc
Terminal Server Configuration
tscc.msc
Terminal Server Licensing
licmgr.exe
Terminal Server Manager
tsadmin.exe
UDDI Services Managment
uddi.msc
Windows Mangement Instumentation
wmimgmt.msc
Wednesday, December 1, 2010
When opening the Word document users are getting error “Word cannot start the converter mswrd632.wpc” or “Cannot load Word for Windows 6.0 files”
When opening the Word document users are getting error “Word cannot start the converter mswrd632.wpc” or “Cannot load Word for Windows 6.0 files”
Problem: - When attempting to open a Word document, users are getting one of following error
1) Word cannot start the converter mswrd632.wpc
2) Cannot load Word for Windows 6.0 files
Cause: - This issue may be started happening after you applied following security update. You may be trying to open a file has the ".doc" file name extension, but the content is a plain text file or another kind of file that is not a Microsoft Word binary file.
Resolution: - The registry fix for this issue is already provided in the KB 973904. Following solution is the updated solution which is provided by Microsoft Word Team. You can use the following steps for the resolution.
Update:- Fix-IT solution for this registry changes is released. Check KB973904
WARNING : If you use Registry Editor incorrectly, you may cause serious problems that may require you to reinstall your operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that you can solve problems that result from using Registry Editor incorrectly. Use Registry Editor at your own risk.
To resolve this issue, an affected user can unregister the mswrd632 converter by editing the registry as follows:
a. Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
b. Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
2. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Shared Tools
\Text Converters\Import\MSWord6.wpc
c. On the Edit menu, click Delete.
d. Click Yes.
e. Exit Registry Editor.
This change will effectively unregister the converter and disable it for third-party applications and for Microsoft Office. Microsoft Office will use its own text converters to open these kinds of files.
==============================================================================================
In case you want to re-enable the converter, you can add an AllowConversion registry entry with a DWORD value of 1. After you set this registry key value to 1, third-party applications can load the Word 6.0/95 for Windows and Macintosh to RTF converter. Please be aware that setting this registry key removes the protection that was added by this security update. Therefore, it should be done only when you trust the source of the files that are loaded by this converter. You can also disable this converter by setting the registry key value to 0.
To do this, follow these steps:
a. Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
b. Locate and then click the following registry subkey. Or, create it if it is not present.
For 32-bit versions of Windows
2. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows
\CurrentVersion\Applets\Wordpad
c. For Microsoft Windows on Windows 64 (WOW) mode
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\microsoft
\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Wordpad
d. On the Edit menu, point to New, and then click DWORD Value.
e. Type AllowConversion for the name of the DWORD, and then press ENTER.
f. Right-click AllowConversion, and then click Modify.
g. In the Value data box, type 1, and then click OK.
h. Exit Registry Editor.
Problem: - When attempting to open a Word document, users are getting one of following error
1) Word cannot start the converter mswrd632.wpc
2) Cannot load Word for Windows 6.0 files
Cause: - This issue may be started happening after you applied following security update. You may be trying to open a file has the ".doc" file name extension, but the content is a plain text file or another kind of file that is not a Microsoft Word binary file.
Resolution: - The registry fix for this issue is already provided in the KB 973904. Following solution is the updated solution which is provided by Microsoft Word Team. You can use the following steps for the resolution.
Update:- Fix-IT solution for this registry changes is released. Check KB973904
WARNING : If you use Registry Editor incorrectly, you may cause serious problems that may require you to reinstall your operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that you can solve problems that result from using Registry Editor incorrectly. Use Registry Editor at your own risk.
To resolve this issue, an affected user can unregister the mswrd632 converter by editing the registry as follows:
a. Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
b. Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
2. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Shared Tools
\Text Converters\Import\MSWord6.wpc
c. On the Edit menu, click Delete.
d. Click Yes.
e. Exit Registry Editor.
This change will effectively unregister the converter and disable it for third-party applications and for Microsoft Office. Microsoft Office will use its own text converters to open these kinds of files.
==============================================================================================
In case you want to re-enable the converter, you can add an AllowConversion registry entry with a DWORD value of 1. After you set this registry key value to 1, third-party applications can load the Word 6.0/95 for Windows and Macintosh to RTF converter. Please be aware that setting this registry key removes the protection that was added by this security update. Therefore, it should be done only when you trust the source of the files that are loaded by this converter. You can also disable this converter by setting the registry key value to 0.
To do this, follow these steps:
a. Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
b. Locate and then click the following registry subkey. Or, create it if it is not present.
For 32-bit versions of Windows
2. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows
\CurrentVersion\Applets\Wordpad
c. For Microsoft Windows on Windows 64 (WOW) mode
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\microsoft
\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Wordpad
d. On the Edit menu, point to New, and then click DWORD Value.
e. Type AllowConversion for the name of the DWORD, and then press ENTER.
f. Right-click AllowConversion, and then click Modify.
g. In the Value data box, type 1, and then click OK.
h. Exit Registry Editor.
Tuesday, September 21, 2010
Migrate MS Outlook Autocomplete cache to new PC or profile
The file is located under
C:\Documents and Settings\\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook\
The folder C:\Documents and Settings\\Application Data\ is hidden and hence choose to show hidden files under “Folder Options”.
Once into the folder look for the file with the extension “NK2″. This filename will be “outlookprofilename.NK2″. For instance, on my PC, outlook profile name is “outlook” and hence the file name is “outlook.NK2″
C:\Documents and Settings\
The folder C:\Documents and Settings\
Once into the folder look for the file with the extension “NK2″. This filename will be “outlookprofilename.NK2″. For instance, on my PC, outlook profile name is “outlook” and hence the file name is “outlook.NK2″
Labels:
auto,
auto-complete,
autocomplete,
email,
nk2,
outlook
Outlook 2007 -Removing an add-in that no longer exists?
Outlook 2007 -Removing an add-in that no longer exists?
Solution 1:
Delete "extend.dat", because the add-ins are cached there.
Go to My Computer (Windows Explorer)
Navigate the menus through: Tools | Folder Options | [View] tab | "Advanced Settings" section | Hidden Files and Folders
Tick (x) Show Hidden Files and Folders, and click [Ok]
In Windows Explorer, navigate to C:\documents and settings\{username}\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Delete "extend.dat"
Close Windows Explorer, and reopen Outlook
Solution 2:
Use the Outlook 2007 Trust Center:
Open Outlook
Navigate the menus through: Tools | Trust Center... | Add-ins (on the left)
Ensure "COM Add-ins" is showing next to "Manage:", at the bottom of the dialog
Click [Go...]
Untick "[ ] The offending extension"
Click [Ok]
Restart Outlook and verify that it worked.
Solution 1:
Delete "extend.dat", because the add-ins are cached there.
Go to My Computer (Windows Explorer)
Navigate the menus through: Tools | Folder Options | [View] tab | "Advanced Settings" section | Hidden Files and Folders
Tick (x) Show Hidden Files and Folders, and click [Ok]
In Windows Explorer, navigate to C:\documents and settings\{username}\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Delete "extend.dat"
Close Windows Explorer, and reopen Outlook
Solution 2:
Use the Outlook 2007 Trust Center:
Open Outlook
Navigate the menus through: Tools | Trust Center... | Add-ins (on the left)
Ensure "COM Add-ins" is showing next to "Manage:", at the bottom of the dialog
Click [Go...]
Untick "[ ] The offending extension"
Click [Ok]
Restart Outlook and verify that it worked.
Friday, September 10, 2010
Pathping
PathPing
PathPing is similar to Tracert except that PathPing is intended to find links that are causing intermittent data loss. PathPing sends packets to each router on the way to a final destination over a period of time and then computes the percentage of packets returned from each hop. Since PathPing shows the degree of packet loss at any given router or link, you can use PathPing to pinpoint which routers or links might be causing network problems.
To use the PathPing utility, at a command prompt type PathPing remote_host, where remote_host is the name or address of a destination computer, server, or router on whose path to which you want to test intermittent data loss.
The following shows a sample PathPing output:
D:\>pathping -n testpc1
Tracing route to testpc1 [7.54.1.196]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
0 172.16.87.35
1 172.16.87.218
2 192.168.52.1
3 192.168.80.1
4 7.54.247.14
5 7.54.1.196
Computing statistics for 25 seconds...
Source to Here This Node/Link
Hop RTT Lost/Sent = Pct Lost/Sent = Pct Address
0 172.16.87.35 0/ 100 = 0% |
1 41ms 0/ 100 = 0% 0/ 100 = 0% 172.16.87.218
13/ 100 = 13% |
2 22ms 16/ 100 = 16% 3/ 100 = 3% 192.168.52.1
0/ 100 = 0% |
3 24ms 13/ 100 = 13% 0/ 100 = 0% 192.168.80.1
0/ 100 = 0% |
4 21ms 14/ 100 = 14% 1/ 100 = 1% 7.54.247.14 0/ 100 = 0% | 5 24ms 13/ 100 = 13%
0/ 100 = 0% 7.54.1.196 Trace complete.
Notice how the output above first lists the five hops on the path to the specified destina- tion and then computes the percentage of data lost over each of these hops. In this case, PathPing shows that data loss at a rate of 13% is occurring between the local computer (172.16.87.35) and the first hop (172.16.87.218).
PathPing is similar to Tracert except that PathPing is intended to find links that are causing intermittent data loss. PathPing sends packets to each router on the way to a final destination over a period of time and then computes the percentage of packets returned from each hop. Since PathPing shows the degree of packet loss at any given router or link, you can use PathPing to pinpoint which routers or links might be causing network problems.
To use the PathPing utility, at a command prompt type PathPing remote_host, where remote_host is the name or address of a destination computer, server, or router on whose path to which you want to test intermittent data loss.
The following shows a sample PathPing output:
D:\>pathping -n testpc1
Tracing route to testpc1 [7.54.1.196]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
0 172.16.87.35
1 172.16.87.218
2 192.168.52.1
3 192.168.80.1
4 7.54.247.14
5 7.54.1.196
Computing statistics for 25 seconds...
Source to Here This Node/Link
Hop RTT Lost/Sent = Pct Lost/Sent = Pct Address
0 172.16.87.35 0/ 100 = 0% |
1 41ms 0/ 100 = 0% 0/ 100 = 0% 172.16.87.218
13/ 100 = 13% |
2 22ms 16/ 100 = 16% 3/ 100 = 3% 192.168.52.1
0/ 100 = 0% |
3 24ms 13/ 100 = 13% 0/ 100 = 0% 192.168.80.1
0/ 100 = 0% |
4 21ms 14/ 100 = 14% 1/ 100 = 1% 7.54.247.14 0/ 100 = 0% | 5 24ms 13/ 100 = 13%
0/ 100 = 0% 7.54.1.196 Trace complete.
Notice how the output above first lists the five hops on the path to the specified destina- tion and then computes the percentage of data lost over each of these hops. In this case, PathPing shows that data loss at a rate of 13% is occurring between the local computer (172.16.87.35) and the first hop (172.16.87.218).
Ping & ICMP
ICMP is, however, blocked by default by Windows Fire- wall in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, and it is also blocked by some routers and stand-alone firewalls. Consequently, to perform adequate troubleshooting of network con- nectivity, you need to ensure that ICMP is not blocked by the remote host. To enable a fire- wall exception for ICMP in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, enable File Sharing in Network and Sharing Center.
If you want to be able to ping a computer, you don't have to turn off the firewall. You only need to TURN ON the file sharing in network sharing center.
If you want to be able to ping a computer, you don't have to turn off the firewall. You only need to TURN ON the file sharing in network sharing center.
Wednesday, August 18, 2010
How to change target location for my Documents
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User Shell Folders
• Click on ‘ Personal’ value in User Shell Folders, change the value data to %HOMESHARE%%HOMEPATH%(This will be the location wherever you want to point your my documents to). Also, apply the same change in Shell Folders.
•If user has pictures stored under home drive server also, then ensure to change My picture value to %HOMESHARE%%HOMEPATH%\my pictures in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders
AND
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User Shell Folders
•Once these have been all done, get user log off and log back in again, the target location of My Document should be corrected.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User Shell Folders
• Click on ‘ Personal’ value in User Shell Folders, change the value data to %HOMESHARE%%HOMEPATH%(This will be the location wherever you want to point your my documents to). Also, apply the same change in Shell Folders.
•If user has pictures stored under home drive server also, then ensure to change My picture value to %HOMESHARE%%HOMEPATH%\my pictures in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders
AND
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User Shell Folders
•Once these have been all done, get user log off and log back in again, the target location of My Document should be corrected.
Open source project - Documenting networks
http://sydiproject.com/
SYDI is the open source project aimed to help you to document your network.
How does SYDI do this?
At the most basic level SYDI consists of a collection of scripts which collects information from your servers and networks, then writes the data to a report.
Documenting a network can seem like a huge project, SYDI helps you get started. Instead of manually collecting information like ip addresses, os version, hardware configuration the scripts collects this automatically it can write directly to Word (or XML).
SYDI is the open source project aimed to help you to document your network.
How does SYDI do this?
At the most basic level SYDI consists of a collection of scripts which collects information from your servers and networks, then writes the data to a report.
Documenting a network can seem like a huge project, SYDI helps you get started. Instead of manually collecting information like ip addresses, os version, hardware configuration the scripts collects this automatically it can write directly to Word (or XML).
Active Desktop
1) Click Start -> Run
2) Type regedit and press enter
3) In the Registry Editor window that appears, please navigate to:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\
Software\
Microsoft\
Internet Explorer\
Desktop\
SafeMode\
Components\
4) Double click on the value "DeskHtmlVersion" and change the entry to 0 and click OK
5) wait for 10 seconds
6) Close the registry editor window
7) left click on the desktop and press F5 to refresh.
2) Type regedit and press enter
3) In the Registry Editor window that appears, please navigate to:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\
Software\
Microsoft\
Internet Explorer\
Desktop\
SafeMode\
Components\
4) Double click on the value "DeskHtmlVersion" and change the entry to 0 and click OK
5) wait for 10 seconds
6) Close the registry editor window
7) left click on the desktop and press F5 to refresh.
Process Explorer
Process Explorer
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896653.aspx?ppud=4
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896653.aspx?ppud=4
Thursday, June 17, 2010
List a user's group membership
List group membership for a user
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>dsget user "CN=Peter Fordyce,OU=Kordia Solutions,OU=Division
s,OU=Prod,DC=internal,DC=local" -memberof > hi.txt
Finding Groups in Which a User Is a Member
Click Start, and then click Run.
In the Open box, type cmd.
At the command prompt, type the following command:
dsget user user_dn -memberof
This command uses the following value:
user_dn specifies the distinguished name of the user object for which you want to display group membership.
To view the complete syntax for this command, at a command prompt, type dsget user /?.
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>dsget user "CN=Peter Fordyce,OU=Kordia Solutions,OU=Division
s,OU=Prod,DC=internal,DC=local" -memberof > hi.txt
Finding Groups in Which a User Is a Member
Click Start, and then click Run.
In the Open box, type cmd.
At the command prompt, type the following command:
dsget user user_dn -memberof
This command uses the following value:
user_dn specifies the distinguished name of the user object for which you want to display group membership.
To view the complete syntax for this command, at a command prompt, type dsget user /?.
Tuesday, June 8, 2010
indows 7 keyboard shortcuts
Windows logo key + R
Add/Remove Programs = appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools = control admintools
Authorization Manager= azman.msc “New”
Calculator = calc
Certificate Manager = certmgr.msc
Character Map = charmap
Check Disk Utility = chkdsk
Control Panel = control ”New”
Command Prompt = cmd.exe
Component Services = dcomcnfg
Computer Management = compmgmt.msc = CompMgmtLauncher ”New”
Date and Time Properties = timedate.cpl
Downloads = Downloads ”New”
Device Manager = devmgmt.msc
Direct X Troubleshooter = dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility = cleanmgr
Defragment User Interface = dfrgui ”New”
Ditilizer Calibration Tool = tabcal ”New”
Disk Management = diskmgmt.msc
Disk Parmelonion Manager = diskpart
Display Properties = control desktop or desk.cpl
DPI Scaling = dpiscaling ”New”
Driver Package Installer = dpinst ”New”
Driver Verifier Utility = verifier or /reset
DVD Player = dvdplay ”New”
Encryption File System = rekeywiz ”New”
Event Viewer = eventvwr.msc
Fax Cover Sheet Editor = fxscover ”New”
File Signature Verification Tool = sigverif
Folders Properties = control folders
Fonts = control fonts
Free Cell Card Game = freecell
Group Policy Editor = gpedit.msc
Internet Explorer = iexplore
Iexpress Wizard = iexpress
Internet Properties = inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration = ipconfig.exe
iSCSI Initiator = iscsicpl ”New”
Keyboard Properties = control keyboard
Libraries = explorer or Windows key + E
Local Security Settings = secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups = lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows = logoff
Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool = msdt ”New”
Microsoft Paint = mspaint.exe
Mouse Properties = control mouse
Mouse Properties = main.cpl
Mobility Center (only on mobile) = mblctr or Windows key + X
Network Connections = control netconnections
Network Connections = ncpa.cpl
Notepad = notepad
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbcad32 ”New”
Optional Features Manager = optionalfeatures ”New”
On Screen Keyboard = osk or Windows key + U
Performance Monitor = perfmon.msc
Phone and Modem Options = telephon.cpl
Power Configuration = powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes = control printers
Printer Migration = PrintBrmUi ”New”
Private Character Editor = eudcedit
Regional Settings = intl.cpl
Registry Editor = regedit.exe
Remote Assistance = msra ”New”
Remote Desktop = mstsc
Resultant Set of Policy = rsop.msc
Scheduled Tasks = control schedtasks
Security Center = wscui.cpl
Services = services.msc
Shared Folders/MMC = fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows = shutdown
Snipping Tool = snippingtool ”New”
Sounds and Audio = mmsys.cpl
Sound Recorder = soundrecorder ”New”
Sound Volume = sndvol ”New”
Spider Solitare Card Game = spider
SQL Client Configuration = cliconfg
Stored User Names and Passwords = credwiz ”New”
Sticky Note = StikyNot ”New”
System Configuration Editor = sysedit
System Configuration Utility = msconfig
System File Checker Utility = sfc
System Information = msinfo32
System Properties = sysdm.cpl or Windows key + Pause/Break
Task Manager = taskmgr
Trusted Platform Module = TpmInit ”New”
Utility Manager = utilman
User Accounts = netplwiz or control userpasswords2
Windows Activation = slui ”New”
Windows Backup Utility = sdclt ”New”
Windows Fax and Scan = wfs ”New”
Windows Firewall = firewall.cpl
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security = wf.msc ”New”
Windows Image Acquisition = wiaacmgr ”New”
Windows Media Player = wmplayer
Windows Magnifier = magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure = wmimgmt.msc
Windows Update App Manager = wuapp ”New”
Windows Standalong Update Manager = wusa ”New’
Windows System Security Tool = syskey
Windows Share Creation Wizard = shrpubw ”New”
Wordpad = write
Add/Remove Programs = appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools = control admintools
Authorization Manager= azman.msc “New”
Calculator = calc
Certificate Manager = certmgr.msc
Character Map = charmap
Check Disk Utility = chkdsk
Control Panel = control ”New”
Command Prompt = cmd.exe
Component Services = dcomcnfg
Computer Management = compmgmt.msc = CompMgmtLauncher ”New”
Date and Time Properties = timedate.cpl
Downloads = Downloads ”New”
Device Manager = devmgmt.msc
Direct X Troubleshooter = dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility = cleanmgr
Defragment User Interface = dfrgui ”New”
Ditilizer Calibration Tool = tabcal ”New”
Disk Management = diskmgmt.msc
Disk Parmelonion Manager = diskpart
Display Properties = control desktop or desk.cpl
DPI Scaling = dpiscaling ”New”
Driver Package Installer = dpinst ”New”
Driver Verifier Utility = verifier or /reset
DVD Player = dvdplay ”New”
Encryption File System = rekeywiz ”New”
Event Viewer = eventvwr.msc
Fax Cover Sheet Editor = fxscover ”New”
File Signature Verification Tool = sigverif
Folders Properties = control folders
Fonts = control fonts
Free Cell Card Game = freecell
Group Policy Editor = gpedit.msc
Internet Explorer = iexplore
Iexpress Wizard = iexpress
Internet Properties = inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration = ipconfig.exe
iSCSI Initiator = iscsicpl ”New”
Keyboard Properties = control keyboard
Libraries = explorer or Windows key + E
Local Security Settings = secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups = lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows = logoff
Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool = msdt ”New”
Microsoft Paint = mspaint.exe
Mouse Properties = control mouse
Mouse Properties = main.cpl
Mobility Center (only on mobile) = mblctr or Windows key + X
Network Connections = control netconnections
Network Connections = ncpa.cpl
Notepad = notepad
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbcad32 ”New”
Optional Features Manager = optionalfeatures ”New”
On Screen Keyboard = osk or Windows key + U
Performance Monitor = perfmon.msc
Phone and Modem Options = telephon.cpl
Power Configuration = powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes = control printers
Printer Migration = PrintBrmUi ”New”
Private Character Editor = eudcedit
Regional Settings = intl.cpl
Registry Editor = regedit.exe
Remote Assistance = msra ”New”
Remote Desktop = mstsc
Resultant Set of Policy = rsop.msc
Scheduled Tasks = control schedtasks
Security Center = wscui.cpl
Services = services.msc
Shared Folders/MMC = fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows = shutdown
Snipping Tool = snippingtool ”New”
Sounds and Audio = mmsys.cpl
Sound Recorder = soundrecorder ”New”
Sound Volume = sndvol ”New”
Spider Solitare Card Game = spider
SQL Client Configuration = cliconfg
Stored User Names and Passwords = credwiz ”New”
Sticky Note = StikyNot ”New”
System Configuration Editor = sysedit
System Configuration Utility = msconfig
System File Checker Utility = sfc
System Information = msinfo32
System Properties = sysdm.cpl or Windows key + Pause/Break
Task Manager = taskmgr
Trusted Platform Module = TpmInit ”New”
Utility Manager = utilman
User Accounts = netplwiz or control userpasswords2
Windows Activation = slui ”New”
Windows Backup Utility = sdclt ”New”
Windows Fax and Scan = wfs ”New”
Windows Firewall = firewall.cpl
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security = wf.msc ”New”
Windows Image Acquisition = wiaacmgr ”New”
Windows Media Player = wmplayer
Windows Magnifier = magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure = wmimgmt.msc
Windows Update App Manager = wuapp ”New”
Windows Standalong Update Manager = wusa ”New’
Windows System Security Tool = syskey
Windows Share Creation Wizard = shrpubw ”New”
Wordpad = write
Clear user's cached password
run netplwiz from run command
thatll open the control panel thing i was looking for
go to the advanced tab
manage passwords
delete all windows passwords
thatll open the control panel thing i was looking for
go to the advanced tab
manage passwords
delete all windows passwords
Monday, June 7, 2010
How to find computer model name/serial number
How to find computer model name/serial number
To retrieve serial number of the computer run the following command from command line
wmic bios get serialnumber
To retrieve model name of the computer run the following command from command line
wmic csproduct get name
This code doesn’t return information for all computers, but I’ve found it very usefull where its available.
Labels:
csproduct,
How to find computer model name,
number,
serial,
serialnumber
Tuesday, June 1, 2010
Unable to Print the whole PDF document
Sunday, May 30, 2010
Create Shared Mailboxes
Creating Shared Mailboxes
The Exchange Management Console does not give the option for creating a shared mailbox in the new mailbox wizard. To create shared mailboxes you must use PowerShell.
To create a shared mailbox you simply add the "-Shared" option while creating the mailbox using the New-Mailbox cmdlet.
[PS] C:\>New-Mailbox -Name:'Help Desk' -OrganizationalUnit:'Domain.com/Exchange Resources' -Database:'Mailbox Database' -UserPrincipalName:'helpdesk@domain.com' -Shared
In this sample, a disabled user account will be created in the 'Exchange Resources' organizational unit with an attached mailbox. Since the user account is disabled by default no initial password was required.
If desired, existing mailboxes can be converted to shared mailboxes using the Set-Mailbox cmdlet by using the -Type parameter.
[PS] C:\>Set-Mailbox helpdesk -Type:Shared
To convert a shared mailbox to a regular user mailbox use the -Type:Regular option.
Assigning Permissions
Shared mailboxes do not have an associated password so you must grant mailbox permissions for the users requiring access to the mailbox. Since, by definition, shared mailboxes will be accessed by multiple users, I suggest assigning permissions using security groups. The first step is to create a security group in your domain containing the users you want to access the shared mailbox. For this example I will name the group "Help Desk Permissions Group". Grant full mailbox permissions for the group you just created.
[PS] C:\>Add-MailboxPermission helpdesk -User:'Help Desk Permissions Group' -AccessRights:FullAccess
Users in the the "Help Desk Permissions Group" will now have full access to the mailbox. But you are not done yet...you MUST also add the active directory 'Send-As' permission so that members of the group can send mail with the shared mailbox's email address. Additionally, you may want to add permissions to read/write personal information so that users can setup delegates if needed.
[PS] C:\>Add-ADPermission helpdesk -User:'Help Desk Permissions Group' -ExtendedRights:Send-As -AccessRights:ReadProperty, WriteProperty -Properties:'Personal Information'
Now your users will have complete access to the shared mailbox.
Example: create the following mailbox:
Name: Pinnacle Parking
Email: pinnacleparking@kordia.com.au
new-mailbox -name "Pinnacle Parking" -database "WINEXMP01\WINEXMP01 SG8\SG8_IS1" -org "internal.local/Prod/Special Objects/Exchange Resources" -shared -UserPrincipalName "pinnacleparking@kordia.com.au"
The Exchange Management Console does not give the option for creating a shared mailbox in the new mailbox wizard. To create shared mailboxes you must use PowerShell.
To create a shared mailbox you simply add the "-Shared" option while creating the mailbox using the New-Mailbox cmdlet.
[PS] C:\>New-Mailbox -Name:'Help Desk' -OrganizationalUnit:'Domain.com/Exchange Resources' -Database:'Mailbox Database' -UserPrincipalName:'helpdesk@domain.com' -Shared
In this sample, a disabled user account will be created in the 'Exchange Resources' organizational unit with an attached mailbox. Since the user account is disabled by default no initial password was required.
If desired, existing mailboxes can be converted to shared mailboxes using the Set-Mailbox cmdlet by using the -Type parameter.
[PS] C:\>Set-Mailbox helpdesk -Type:Shared
To convert a shared mailbox to a regular user mailbox use the -Type:Regular option.
Assigning Permissions
Shared mailboxes do not have an associated password so you must grant mailbox permissions for the users requiring access to the mailbox. Since, by definition, shared mailboxes will be accessed by multiple users, I suggest assigning permissions using security groups. The first step is to create a security group in your domain containing the users you want to access the shared mailbox. For this example I will name the group "Help Desk Permissions Group". Grant full mailbox permissions for the group you just created.
[PS] C:\>Add-MailboxPermission helpdesk -User:'Help Desk Permissions Group' -AccessRights:FullAccess
Users in the the "Help Desk Permissions Group" will now have full access to the mailbox. But you are not done yet...you MUST also add the active directory 'Send-As' permission so that members of the group can send mail with the shared mailbox's email address. Additionally, you may want to add permissions to read/write personal information so that users can setup delegates if needed.
[PS] C:\>Add-ADPermission helpdesk -User:'Help Desk Permissions Group' -ExtendedRights:Send-As -AccessRights:ReadProperty, WriteProperty -Properties:'Personal Information'
Now your users will have complete access to the shared mailbox.
Example: create the following mailbox:
Name: Pinnacle Parking
Email: pinnacleparking@kordia.com.au
new-mailbox -name "Pinnacle Parking" -database "WINEXMP01\WINEXMP01 SG8\SG8_IS1" -org "internal.local/Prod/Special Objects/Exchange Resources" -shared -UserPrincipalName "pinnacleparking@kordia.com.au"
Monday, May 24, 2010
Thursday, May 13, 2010
How To Recall a Sent Message in Outlook 2007
1. Click on Sent Items.
2. Find the message you want recalled and double-click it to open.
3. Go to the Ribbon.
4. In the Actions section, click Other Actions and select Recall This Message.
5. Select Delete unread copies of this message.
6. To be notified about the success of the recall, check the Tell me if recall succeeds or fails for each recipient checkbox.
7. Click OK.
2. Find the message you want recalled and double-click it to open.
3. Go to the Ribbon.
4. In the Actions section, click Other Actions and select Recall This Message.
5. Select Delete unread copies of this message.
6. To be notified about the success of the recall, check the Tell me if recall succeeds or fails for each recipient checkbox.
7. Click OK.
Monday, April 19, 2010
display group memberships for a user
dsget user "cn=M T,ou=users,ou=disabled objects, dc=internal,dc=local" -memberof -expand >>MT.txt
move MT.txt desktop
move MT.txt desktop
Display members who have access to a folder
If it's a network drive, map it as T drive then type in
cacls t:/
Source
http://ss64.com/nt/xcalcs.html
cacls t:/
Source
http://ss64.com/nt/xcalcs.html
Wednesday, April 14, 2010
Active Directory: Copy Distribution List Members to Another Distribution List
Summary: In this example, we will copy all members from one Distribution Group to another Distribution Group.
Copy the contents below and save as copymembers.vbs to C: drive
Const ADS_GROUP_TYPE_GLOBAL_GROUP = &H2
Set objOU = GetObject("LDAP://OU=Security Groups, dc=company, dc=com")
Set objOldGroup = GetObject("LDAP://CN=mysourcegroup, ou=security groups, dc=company, dc=com")
Set objNewGroup = GetObject("LDAP://CN=mytargetgroup, ou=security groups, dc=company, dc=com")
On Error Resume Next
For Each objUser in objOldGroup.Member
objNewGroup.Add "LDAP://" & objUser
Next
Open Command prompt:
C:\>cscript copymembers.vbs
The script will copy all members in the "mysourcegroup" Distribution List to your "mytargetgroup" Distribution List.
Note: Some organizations like to use # in front of their Distribution List names so they appear together in the GAL. Because this is a special character it will need to be in double quotes to treat # as a literal.
Example:
("LDAP://""CN=mysourcegroup""
James Chong (MVP)MCSE M+, S+, MCTS, Security+
msexchangetips.blogspot.com
Copy the contents below and save as copymembers.vbs to C: drive
Const ADS_GROUP_TYPE_GLOBAL_GROUP = &H2
Set objOU = GetObject("LDAP://OU=Security Groups, dc=company, dc=com")
Set objOldGroup = GetObject("LDAP://CN=mysourcegroup, ou=security groups, dc=company, dc=com")
Set objNewGroup = GetObject("LDAP://CN=mytargetgroup, ou=security groups, dc=company, dc=com")
On Error Resume Next
For Each objUser in objOldGroup.Member
objNewGroup.Add "LDAP://" & objUser
Next
Open Command prompt:
C:\>cscript copymembers.vbs
The script will copy all members in the "mysourcegroup" Distribution List to your "mytargetgroup" Distribution List.
Note: Some organizations like to use # in front of their Distribution List names so they appear together in the GAL. Because this is a special character it will need to be in double quotes to treat # as a literal.
Example:
("LDAP://""CN=mysourcegroup""
James Chong (MVP)MCSE M+, S+, MCTS, Security+
msexchangetips.blogspot.com
List member of a group in exchange
dsget group "DN_of_group" -members -expand > userlist.txt
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>dsget group "CN=Sales - Products & Services,OU=Security Grou
ps,OU=Groups,OU=Prod,DC=internal,DC=local" -members -expand > userlist.txt
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>move userlist.txt C:\Users\jqiu-admin\Desktop\temp
1 file(s) moved.
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>dsget group "CN=Sales - Products & Services,OU=Security Grou
ps,OU=Groups,OU=Prod,DC=internal,DC=local" -members -expand > userlist.txt
C:\Users\jqiu-admin>move userlist.txt C:\Users\jqiu-admin\Desktop\temp
1 file(s) moved.
Copy group membership of a user to another user
1) Download the VB script from here:
http://www.windowsitpro.com/article/active-directory-service-interfaces-adsi/copy-group-memberships-from-one-ad-user-to-another.aspx
2) Save the script to C drive;
3) Open up an command prompt;
C:\>cscript Copymembership.vbs existingEmployee newEmployee
where ntid1 is the existing employee's username and ntid2 is the new employee's username.
http://www.windowsitpro.com/article/active-directory-service-interfaces-adsi/copy-group-memberships-from-one-ad-user-to-another.aspx
2) Save the script to C drive;
3) Open up an command prompt;
C:\>cscript Copymembership.vbs existingEmployee newEmployee
where ntid1 is the existing employee's username and ntid2 is the new employee's username.
Sunday, April 11, 2010
How to restore the sent item mailbox in outlook
You need to download this exe file(MFCMAPI 32 bit executable - March 2010 (6.0.0.18)) from here:
http://mfcmapi.codeplex.com/releases/view/41828
Extra then install it.
Look for mailbox
Double click PR_ATTR_HIDDEN and uncheck the "Boolean" box and click OK -> set the value to false. If it's true then your sent item mailbox won't show.
Correct the registry value using the information from the following article from the Knowedge Base online to prevent future issues with any users moved to the impacted Back-End Exchange Server:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;311154 (http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;311154)
To immediately correct the problem for existing users, you can use the following steps using MFCMAPI.EXE:
Launch MFCMAPI and click OK to the first window.
Click Session, click Log On and Display Store Table.
Choose the Outlook profile for the mailbox and click OK, provide credentials if prompted.
Double click the Mailbox - and a new window will open.
Expand the Root Folder .
Expand Top Of Information Store.
Single click to select the impacted folder - for example Contacts.
In the detail window, note the value of the PR_ATTR_HIDDEN property (T or F - T means it is Hidden).
Double click PR_ATTR_HIDDEN and uncheck the "Boolean" box and click OK.
Close all MFCMAPI windows and log off Outlook and restart.
The Contacts (or other) folder will be visible and the shortcuts will now work.
Reference:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/924226/en-us
http://mfcmapi.codeplex.com/releases/view/41828
Extra then install it.
Look for mailbox
Double click PR_ATTR_HIDDEN and uncheck the "Boolean" box and click OK -> set the value to false. If it's true then your sent item mailbox won't show.
Correct the registry value using the information from the following article from the Knowedge Base online to prevent future issues with any users moved to the impacted Back-End Exchange Server:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;311154 (http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;311154)
To immediately correct the problem for existing users, you can use the following steps using MFCMAPI.EXE:
Launch MFCMAPI and click OK to the first window.
Click Session, click Log On and Display Store Table.
Choose the Outlook profile for the mailbox and click OK, provide credentials if prompted.
Double click the Mailbox -
Expand the Root Folder .
Expand Top Of Information Store.
Single click to select the impacted folder - for example Contacts.
In the detail window, note the value of the PR_ATTR_HIDDEN property (T or F - T means it is Hidden).
Double click PR_ATTR_HIDDEN and uncheck the "Boolean" box and click OK.
Close all MFCMAPI windows and log off Outlook and restart.
The Contacts (or other) folder will be visible and the shortcuts will now work.
Reference:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/924226/en-us
Tuesday, April 6, 2010
Where to find the command prompt in windows?
Find command prompt: \\ComputerName\c$\WINDOWS\system32
It is the ipconfig.exe file.
Type in set in command prompt:
C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin>set
ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\All Users
APPDATA=C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin\Application Data
CLIENTNAME=D735054T
ClusterLog=C:\WINDOWS\Cluster\cluster.log
CommonProgramFiles=C:\Program Files\Common Files
COMPUTERNAME=AXONREMOTE-K1
ComSpec=C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe
EXCHICONS=C:\Program Files\Exchsrvr\bin\maildsmx.dll
FP_NO_HOST_CHECK=NO
HOMEDRIVE=C:
HOMEPATH=\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin
LOGONSERVER=\\WINDCP18
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=2
OS=Windows_NT
Path=C:\Program Files\HP\NCU;C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\WINDOWS\System32\
Wbem;C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0;C:\Program Files\System Center O
perations Manager 2007\;C:\Program Files\Windows Imaging\
PATHEXT=.COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.PSC1
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=x86
PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=x86 Family 15 Model 2 Stepping 5, GenuineIntel
PROCESSOR_LEVEL=15
PROCESSOR_REVISION=0205
ProgramFiles=C:\Program Files
PROMPT=$P$G
SESSIONNAME=RDP-Tcp#42
SystemDrive=C:
SystemRoot=C:\WINDOWS
TEMP=C:\DOCUME~1\JQIU-A~1\LOCALS~1\Temp\2
TMP=C:\DOCUME~1\JQIU-A~1\LOCALS~1\Temp\2
UATDATA=C:\WINDOWS\system32\CCM\UATData\D9F8C395-CAB8-491d-B8AC-179A1FE1BE77
USERDNSDOMAIN=INTERNAL.LOCAL
USERDOMAIN=INTERNAL
USERNAME=jqiu-admin
USERPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin
windir=C:\WINDOWS
Look at what's under path then put it under envrionment -
A more permanent way to manage environment variables is provided in the System Properties dialog box. Open Control Panel-Performance and Maintenance-System (or right-click on My Computer and choose "Properties"). In the box that opens, click the "Advanced" tab to obtain the dialog box shown below. Next, click the button "Environment Variables".
For more information, click this link below:
http://vlaurie.com/computers2/Articles/environment.htm
It is the ipconfig.exe file.
Type in set in command prompt:
C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin>set
ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\All Users
APPDATA=C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin\Application Data
CLIENTNAME=D735054T
ClusterLog=C:\WINDOWS\Cluster\cluster.log
CommonProgramFiles=C:\Program Files\Common Files
COMPUTERNAME=AXONREMOTE-K1
ComSpec=C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe
EXCHICONS=C:\Program Files\Exchsrvr\bin\maildsmx.dll
FP_NO_HOST_CHECK=NO
HOMEDRIVE=C:
HOMEPATH=\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin
LOGONSERVER=\\WINDCP18
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=2
OS=Windows_NT
Path=C:\Program Files\HP\NCU;C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\WINDOWS\System32\
Wbem;C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0;C:\Program Files\System Center O
perations Manager 2007\;C:\Program Files\Windows Imaging\
PATHEXT=.COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.PSC1
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=x86
PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=x86 Family 15 Model 2 Stepping 5, GenuineIntel
PROCESSOR_LEVEL=15
PROCESSOR_REVISION=0205
ProgramFiles=C:\Program Files
PROMPT=$P$G
SESSIONNAME=RDP-Tcp#42
SystemDrive=C:
SystemRoot=C:\WINDOWS
TEMP=C:\DOCUME~1\JQIU-A~1\LOCALS~1\Temp\2
TMP=C:\DOCUME~1\JQIU-A~1\LOCALS~1\Temp\2
UATDATA=C:\WINDOWS\system32\CCM\UATData\D9F8C395-CAB8-491d-B8AC-179A1FE1BE77
USERDNSDOMAIN=INTERNAL.LOCAL
USERDOMAIN=INTERNAL
USERNAME=jqiu-admin
USERPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\jqiu-admin
windir=C:\WINDOWS
Look at what's under path then put it under envrionment -
A more permanent way to manage environment variables is provided in the System Properties dialog box. Open Control Panel-Performance and Maintenance-System (or right-click on My Computer and choose "Properties"). In the box that opens, click the "Advanced" tab to obtain the dialog box shown below. Next, click the button "Environment Variables".
For more information, click this link below:
http://vlaurie.com/computers2/Articles/environment.htm
Saturday, April 3, 2010
Why can't I join my computer to the domain?
I have a Win2k8 server - server1, got DNS and ADDS installed.
Domain name server.com.
I got another Win2k8 server - server2, can ping server.com but why can't I join it to the domain?
--> check your DNS on server2, make sure it's pointing to the server1's ip not the router's IP!
Domain name server.com.
I got another Win2k8 server - server2, can ping server.com but why can't I join it to the domain?
--> check your DNS on server2, make sure it's pointing to the server1's ip not the router's IP!
Thursday, March 18, 2010
Rebuild WMI database
Originated from SCCM client's error:
Setup was unable to create the WMI namespace CCM The error code is 80041002
There are several ways to clean/rebuilt WMI.
A) Simple rebuilt of WMI repository
This is the short version...
1. stop WMI service-> look up the command for that
2. rename the Repository subdirectory in %windir%\system32\wbem
3. rebuilt the WMI Repository in:
starting wbemtest.exe
connecting using Root/Default
The first connection will take some time since the repository is being rebuilt, but you should connect to a brand new repository afterwards
Additional info:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/scriptcenter/topics/help/wmi.mspx
B) Complete reinstall of WMI
The steps generally include the following:
1. winmgmt /clearadap
2. winmgmt /kill
3. winmgmt /unregserver
4. winmgmt /regserver
5. winmgmt /resyncperf
6. net stop winmgmt
7. del %SystemRoot%/system32/Wbem/Repository/*.* /s
8. net start winmgmt
9. %SystemRoot%/system32/wbem/wbemtest.exe
Setup was unable to create the WMI namespace CCM The error code is 80041002
There are several ways to clean/rebuilt WMI.
A) Simple rebuilt of WMI repository
This is the short version...
1. stop WMI service-> look up the command for that
2. rename the Repository subdirectory in %windir%\system32\wbem
3. rebuilt the WMI Repository in:
starting wbemtest.exe
connecting using Root/Default
The first connection will take some time since the repository is being rebuilt, but you should connect to a brand new repository afterwards
Additional info:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/scriptcenter/topics/help/wmi.mspx
B) Complete reinstall of WMI
The steps generally include the following:
1. winmgmt /clearadap
2. winmgmt /kill
3. winmgmt /unregserver
4. winmgmt /regserver
5. winmgmt /resyncperf
6. net stop winmgmt
7. del %SystemRoot%/system32/Wbem/Repository/*.* /s
8. net start winmgmt
9. %SystemRoot%/system32/wbem/wbemtest.exe
Wednesday, February 10, 2010
Connect to file servers on a MAC
Follow these steps:
Click the Finder icon in the Dock.
Choose Connect to Server from the Go menu (see Note 1).
In the address field of the Connect to Server dialog, type the URL using this syntax (see Note 3):
smb://ServerName/ShareName/
smb://the ip address of your file server
Click the Finder icon in the Dock.
Choose Connect to Server from the Go menu (see Note 1).
In the address field of the Connect to Server dialog, type the URL using this syntax (see Note 3):
smb://ServerName/ShareName/
smb://the ip address of your file server
Friday, January 29, 2010
Thursday, January 28, 2010
AC and DC
This is an image of the AC symbol.
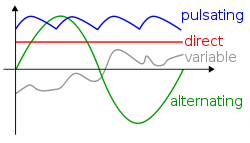
This is an image of the DC symbol.
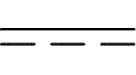
Things to bear in mind:
1) You will never plug a DC power pack to a AC device! Never MIX! In other words, AC goes with AC, DC power pack goes with DC device.
2) Voltages on the device and the power pack have to match. (eg: 12V on the device and 12 V on the power pack)
3) A stands for amperage, the amperage on the power pack must be greater than the amerage on th device otherwise you don't get enough power!
4) You look the output on the adaptor and the input on the device
5) Sometimes you need to look at the symbols to find out whether it's a DC or AC adaptor.
Examples:
Find a power pack for this Thin Client: input DC 12V 3.33A
Power adaptor 1: 4.5V 600mA -> won't match because 4.5V < 12V
Power adaptor 2: 12V 2.0 A -> 12V is ok but it won't match because 2.0A < 3.33A, the amperage has to be greater than the thin client's input amerage.
Answer: the power pack must have an output of 12V and amerage > 3.33A
Other things useful to know:
Most Adaptors (not all) are DC.
Car Batteries are DC.
1000mA = 1A
660mA = 0.66A
3.33A = 3330mA
AC stands for Alternating Current
DC stands for Direct Current
All the batteries in the wolrd are DC.
V= Voltage = pressure of the wire

This is an image of the DC symbol.

Things to bear in mind:
1) You will never plug a DC power pack to a AC device! Never MIX! In other words, AC goes with AC, DC power pack goes with DC device.
2) Voltages on the device and the power pack have to match. (eg: 12V on the device and 12 V on the power pack)
3) A stands for amperage, the amperage on the power pack must be greater than the amerage on th device otherwise you don't get enough power!
4) You look the output on the adaptor and the input on the device
5) Sometimes you need to look at the symbols to find out whether it's a DC or AC adaptor.
Examples:
Find a power pack for this Thin Client: input DC 12V 3.33A
Power adaptor 1: 4.5V 600mA -> won't match because 4.5V < 12V
Power adaptor 2: 12V 2.0 A -> 12V is ok but it won't match because 2.0A < 3.33A, the amperage has to be greater than the thin client's input amerage.
Answer: the power pack must have an output of 12V and amerage > 3.33A
Other things useful to know:
Most Adaptors (not all) are DC.
Car Batteries are DC.
1000mA = 1A
660mA = 0.66A
3.33A = 3330mA
AC stands for Alternating Current
DC stands for Direct Current
All the batteries in the wolrd are DC.
V= Voltage = pressure of the wire
Thursday, January 21, 2010
Bypassing the Logon Screen
1) At a command prompt, type netplwiz to open Advanced User Accounts.
2)On the Users tab, clear the Users Must Enter A User Name And Password To Use This Computer check box and then click OK. Note that the Users Must Enter A User Name And Password To Use This Computer check box doesn't appear if your computer is a member of a domain. Only computers that aren't part of a network or are part of a workgroup can bypass the logon screen. Domain users must enter a user name and password, even to log on locally.
The Automatically Log On dialog box appears.
3)Type the user name and password for the account that you want to be logged on each time you start your computer.
2)On the Users tab, clear the Users Must Enter A User Name And Password To Use This Computer check box and then click OK. Note that the Users Must Enter A User Name And Password To Use This Computer check box doesn't appear if your computer is a member of a domain. Only computers that aren't part of a network or are part of a workgroup can bypass the logon screen. Domain users must enter a user name and password, even to log on locally.
The Automatically Log On dialog box appears.
3)Type the user name and password for the account that you want to be logged on each time you start your computer.
Making the Logon Text Bigger
If you use a high-DPI setting to enlarge text while you're logged on, you might be disappointed to see that your setting doesn't apply to the logon screen. To remedy that situation, follow these steps:
In the Start menu search box, type regedit and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
In Registry Editor, navigate to the HKU\.Default\Control Panel\Desktop key.
If a DWORD value named LogPixels does not exist, create one.
Double-click the LogPixels value. Be sure that Base is set to Decimal, and then set the value to the desired resolution in dots per inch. The default setting is 96 DPI; larger values increase the text size. For example, setting the value to 120 increases the size by 25 percent. (96 times 1.25 is 120.)
Log off to see the changes. The first time each user logs on after making this change, Windows applies the new DPI setting to the user's desktop as well as the logon screen. Users who want to change to a different text size can do so by visiting Display in Control Panel. For details, see "Making Text Easier to Read" on page 143.
In the Start menu search box, type regedit and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
In Registry Editor, navigate to the HKU\.Default\Control Panel\Desktop key.
If a DWORD value named LogPixels does not exist, create one.
Double-click the LogPixels value. Be sure that Base is set to Decimal, and then set the value to the desired resolution in dots per inch. The default setting is 96 DPI; larger values increase the text size. For example, setting the value to 120 increases the size by 25 percent. (96 times 1.25 is 120.)
Log off to see the changes. The first time each user logs on after making this change, Windows applies the new DPI setting to the user's desktop as well as the logon screen. Users who want to change to a different text size can do so by visiting Display in Control Panel. For details, see "Making Text Easier to Read" on page 143.
Setting a Custom Desktop Background
Method 1:
http://tweaks.com/software/tweakslogon/
Method 2:
To use a desktop background other than the default image shown in Figure 16-7 (or one provided by the manufacturer of your computer), follow these steps:
In the Start menu search box, type regedit and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
In Registry Editor, navigate to the HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI\Background key.
If a DWORD value named OEMBackground does not exist, create one. Set this value's data to 1.
In Windows Explorer, navigate to %Windir%\System32\Oobe\Info\Backgrounds. (If the subfolders of Oobe do not exist, create them.)
Copy the image you want to this folder, using these guidelines:
The image must be in jpg format, and the file size cannot exceed 256 KB.
Scale the image to the pixel dimensions of your primary monitor's native (or default) resolution, and name the file Backgroundwwwxhhh.jpg, where www and hhh represent the width and height, in pixels (for example, Background1600x1200.jpg).
Because this feature doesn't support all screen resolutions, create a copy of the image file and name it BackgroundDefault.jpg. If Windows is unable to use the resolution-specific image, it uses this one and stretches it to fit.
If that procedure sounds too daunting, download the Tweaks.com Logon Changer, a utility that compresses your image file (to stay under the file-size limit) as well as safely diving into the registry and deeply nested folders for you. Get it from w7io.com/1603.
http://tweaks.com/software/tweakslogon/
Method 2:
To use a desktop background other than the default image shown in Figure 16-7 (or one provided by the manufacturer of your computer), follow these steps:
In the Start menu search box, type regedit and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
In Registry Editor, navigate to the HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI\Background key.
If a DWORD value named OEMBackground does not exist, create one. Set this value's data to 1.
In Windows Explorer, navigate to %Windir%\System32\Oobe\Info\Backgrounds. (If the subfolders of Oobe do not exist, create them.)
Copy the image you want to this folder, using these guidelines:
The image must be in jpg format, and the file size cannot exceed 256 KB.
Scale the image to the pixel dimensions of your primary monitor's native (or default) resolution, and name the file Backgroundwwwxhhh.jpg, where www and hhh represent the width and height, in pixels (for example, Background1600x1200.jpg).
Because this feature doesn't support all screen resolutions, create a copy of the image file and name it BackgroundDefault.jpg. If Windows is unable to use the resolution-specific image, it uses this one and stretches it to fit.
If that procedure sounds too daunting, download the Tweaks.com Logon Changer, a utility that compresses your image file (to stay under the file-size limit) as well as safely diving into the registry and deeply nested folders for you. Get it from w7io.com/1603.
Hide the name of the last user to log on
Inside Out: Hide the name of the last user to log on
On a computer joined to a domain, by default the name and picture of the last user who logged on appears on the logon screen. On a system that's used primarily by a single user, this is a convenient feature that allows the user to log on again without typing his or her name each time. For a computer that's shared by many users, you might prefer not to show the last user. You can prevent the last-used name from appearing by typing secpol.msc at an elevated command prompt to open Local Security Policy. In Local Security Policy, open Local Policies\Security Options. Then enable the policy setting named Interactive Logon: Do Not Display Last User Name.
On a computer joined to a domain, by default the name and picture of the last user who logged on appears on the logon screen. On a system that's used primarily by a single user, this is a convenient feature that allows the user to log on again without typing his or her name each time. For a computer that's shared by many users, you might prefer not to show the last user. You can prevent the last-used name from appearing by typing secpol.msc at an elevated command prompt to open Local Security Policy. In Local Security Policy, open Local Policies\Security Options. Then enable the policy setting named Interactive Logon: Do Not Display Last User Name.
Working with UAC
Advanced User Accounts If your computer is joined to a domain, clicking the Manage User Accounts link in User Accounts opens Advanced User Accounts. (The title bar of the dialog box doesn't include the word Advanced, however.) If your computer is not joined to a domain, you can open this version by typing netplwiz at a command prompt.
Local Users And Groups This Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in—which is available only in Windows 7 Professional, Ultimate, and Enterprise editions—provides access to more account management features than User Accounts and is friendlier than command-line utilities. You can start Local Users And Groups, shown in Figure 16-5, in any of the following ways:
In Computer Management, open System Tools, Local Users And Groups.
At a command prompt, type lusrmgr.msc.
In Advanced User Accounts, click the Advanced tab, and then click the Advanced button.
Local Users And Groups This Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in—which is available only in Windows 7 Professional, Ultimate, and Enterprise editions—provides access to more account management features than User Accounts and is friendlier than command-line utilities. You can start Local Users And Groups, shown in Figure 16-5, in any of the following ways:
In Computer Management, open System Tools, Local Users And Groups.
At a command prompt, type lusrmgr.msc.
In Advanced User Accounts, click the Advanced tab, and then click the Advanced button.
Tuesday, January 19, 2010
Donwside of dual-boot
If you've set up a dual-boot system with Windows XP and Windows 7 (or Windows Vista) on the same system, you should be aware of one unfortunate side effect caused by this configuration. When you boot into Windows XP, the system wipes out all restore points created by the later Windows version. New restore points are created at the usual times when you return to Windows 7, but all previous restore points are gone. This unfortunate state of affairs is caused because Windows XP doesn't recognize the format of the newer restore points; assuming they're corrupt, it deletes them and creates new ones.
Create a virtual disk
In the Backup And Restore Control Panel, click Create A System Image in the left pane and follow the prompts to select a backup destination. The disk space requirements for an image-based backup can be substantial. Windows will warn you if the destination you choose doesn't have sufficient free disk space.
System images are stored in virtual hard drive (.vhd) format. Although the data is not compressed, it is compact because the image file does not include the hard drive's unused space and some other unnecessary files, such as hibernation files, page files, and restore points. Incremental system image backups on a local drive are not written to a separate folder. Instead, new and updated files (actually, the changed blocks in those files) are written to the same .vhd file. The older blocks are stored as shadow copies in the .vhd file, allowing you to restore any previous version.
System images are stored in virtual hard drive (.vhd) format. Although the data is not compressed, it is compact because the image file does not include the hard drive's unused space and some other unnecessary files, such as hibernation files, page files, and restore points. Incremental system image backups on a local drive are not written to a separate folder. Instead, new and updated files (actually, the changed blocks in those files) are written to the same .vhd file. The older blocks are stored as shadow copies in the .vhd file, allowing you to restore any previous version.
Single User Mode / Multi-user Mode
Change to single user mode: change user /install (When you want to install/uninstall a program)
Chnage to multi-user mode: change user /execute
Chnage to multi-user mode: change user /execute
Encrypt your hard drive using BitLocker
Don't have TPM(Trusted Platform Module)? No worries, here is the link shows you how to encrypt your HDD:
http://blogs.techrepublic.com.com/networking/?p=2248&tag=rbxccnbtr1
http://blogs.techrepublic.com.com/networking/?p=2248&tag=rbxccnbtr1
Files that do not go to the recycle bin
The following kinds of deletions do not go to the Recycle Bin:
Files stored on removable disks
Files stored on network drives, even when that volume is on a computer that has its own Recycle Bin
Files deleted from a command prompt
Files deleted from compressed (zipped) folders
Files stored on removable disks
Files stored on network drives, even when that volume is on a computer that has its own Recycle Bin
Files deleted from a command prompt
Files deleted from compressed (zipped) folders
What does an index do?
The index is constructed dynamically by the Windows Search service, Search-Indexer.exe. The indexer crawls through all locations that are prescribed to be indexed, converting the content of documents (in supported formats) into plain text and then storing the text and metadata for quick retrieval.
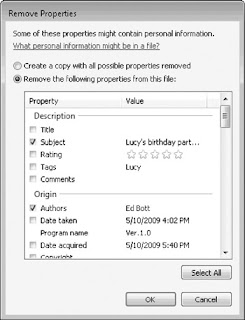
Remove personal metadata for privacy's sake
Some useful shortcuts
F11 Maximize
Windows logo key + E to open Windows Explorer
Inside Out: Zip through Windows Explorer with keyboard shortcuts
Pressing Ctrl+N in Windows Explorer opens a new window on the same folder. Ctrl + W closes the current window. (These keyboard shortcuts function the same way in Internet Explorer.) The following additional keyboard shortcuts work in Windows Explorer:
Alt+Up Arrow—Go up one level.
Alt+Right Arrow—Go forward.
Alt+Left Arrow—Go back.
Alt+D—Move the focus to the address bar, and select the current path.
F4—Move the insertion point to the address bar, and display the contents of the drop-down list of previous addresses.
Alt+Enter—Show properties of the selected file.
Shift+F10—Open the shortcut menu for the current selection (which is the same as a right-click).
F6—Cycle through the following elements: address bar, toolbar, navigation pane, file list, column headings (available in Details view only).
Tab—Cycle through the following elements: address bar, search box, toolbar, navigation pane, file list, column headings (available in Details view only).
F11—Toggle full-screen mode.
Ctrl+Shift+N—Create a new subfolder in the current folder.
Ctrl+Shift+E—Expands navigation pane to the current folder.
Windows logo key + E to open Windows Explorer
Inside Out: Zip through Windows Explorer with keyboard shortcuts
Pressing Ctrl+N in Windows Explorer opens a new window on the same folder. Ctrl + W closes the current window. (These keyboard shortcuts function the same way in Internet Explorer.) The following additional keyboard shortcuts work in Windows Explorer:
Alt+Up Arrow—Go up one level.
Alt+Right Arrow—Go forward.
Alt+Left Arrow—Go back.
Alt+D—Move the focus to the address bar, and select the current path.
F4—Move the insertion point to the address bar, and display the contents of the drop-down list of previous addresses.
Alt+Enter—Show properties of the selected file.
Shift+F10—Open the shortcut menu for the current selection (which is the same as a right-click).
F6—Cycle through the following elements: address bar, toolbar, navigation pane, file list, column headings (available in Details view only).
Tab—Cycle through the following elements: address bar, search box, toolbar, navigation pane, file list, column headings (available in Details view only).
F11—Toggle full-screen mode.
Ctrl+Shift+N—Create a new subfolder in the current folder.
Ctrl+Shift+E—Expands navigation pane to the current folder.
Monday, January 18, 2010
Thursday, January 14, 2010
Windows 7 compatibility Mode
Use hotmail with outlook
http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/outlook/HA102218231033.aspx
Key: download MS office outlook connector
Key: download MS office outlook connector
Saturday, January 9, 2010
Rest PAP2T
1. Plug phone into one of the line ports
2. Lift handset and dial **** to enter the IRV
3. dial RESET# (73738#) to factory reset
4. dial 1 to confirm
5. Hang up, the PAP2T should reset and now be accessible
now you don't need a user name and password to swtich to admin mode.
2. Lift handset and dial **** to enter the IRV
3. dial RESET# (73738#) to factory reset
4. dial 1 to confirm
5. Hang up, the PAP2T should reset and now be accessible
now you don't need a user name and password to swtich to admin mode.
Scan local LAN IPs
http://download.cnet.com/Advanced-IP-Scanner/3000-2085_4-10115592.html?part=dl-73294&subj=dl&tag=button
Advanced IP Scanner 1.5
Very good tool
Advanced IP Scanner 1.5
Very good tool
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)